
Most preganglionic neurons in the sympathetic nervous system originate in the spinal cord. Examples of functions controlled by the sympathetic nervous system include an accelerated heart rate and inhibited digestion, both of which help prepare an organism's body for the physical strain required to escape a potentially dangerous situation or to fend off a predator. One way to remember this is to think of the surprise a person feels when encountering a snake ("snake" and "sympathetic" both begin with "s").

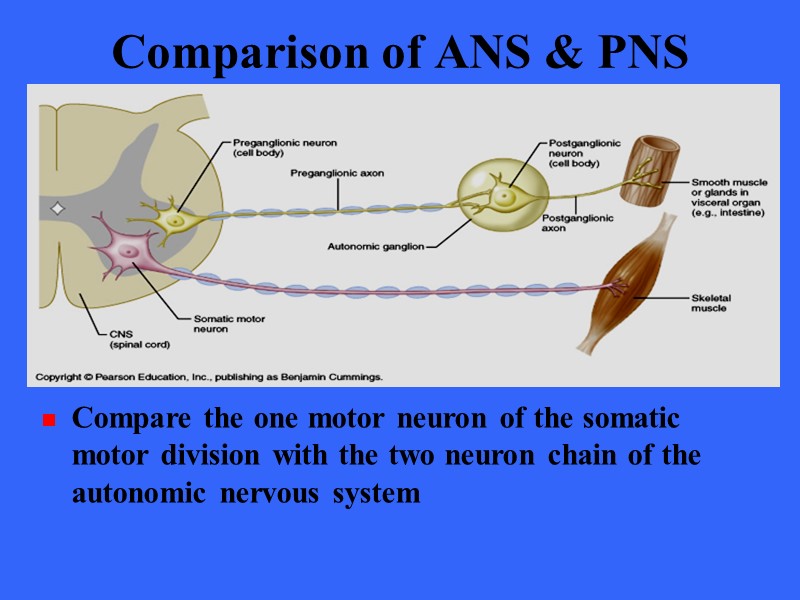
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the "fight or flight" response that occurs when an animal encounters a dangerous situation. The postganglionic neuron, in turn, acts on a target organ. In the autonomic nervous system, a preganglionic neuron of the CNS synapses with a postganglionic neuron of the parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic system activates the "fight or flight" response, while the parasympathetic system activates the "rest and digest" response. There are two divisions of the autonomic nervous system that often have opposing effects: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system.Īutonomic nervous system: Autonomic responses are mediated by the sympathetic and the parasympathetic systems, which are antagonistic to one another. A preganglionic neuron (originating in the CNS) synapses to a neuron in a ganglion that, in turn, synapses on the target organ. Signaling to the target tissue usually involves two synapses. It can continuously monitor the conditions of these different systems and implement changes as needed. It controls the lungs, the heart, smooth muscle, and exocrine and endocrine glands, largely without conscious control. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) serves as the relay between the central nervous system (CNS) and the internal organs.
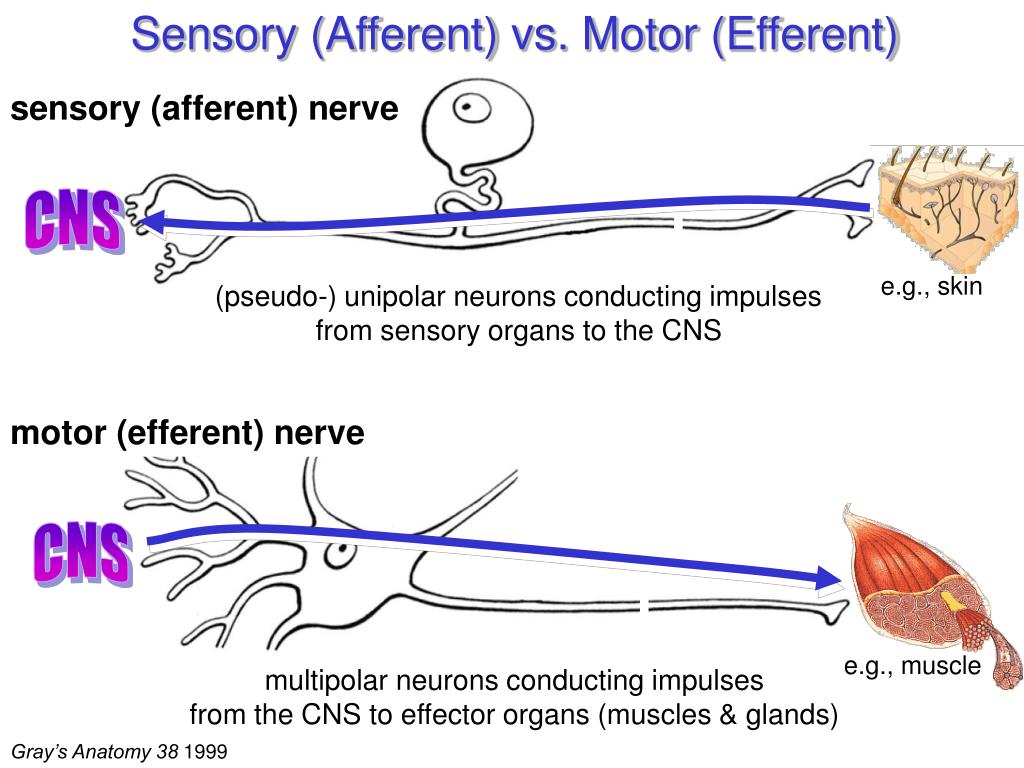
parasympathetic nervous system: one of the divisions of the autonomic nervous system, based between the brain and the spinal cord, that slows the heart and relaxes muscles.sympathetic nervous system: the part of the autonomic nervous system that under stress raises blood pressure and heart rate, constricts blood vessels and dilates the pupils.preganglionic: describing the nerve fibres that supply a ganglion.The parasympathetic nervous system works in opposition to the sympathetic during periods of rest it slows the heart rate, lowers the blood pressure, stimulates digestion, and moves blood flow back to the skin.The sympathetic nervous system controls the body's automatic response to danger, increasing the heart rate, dilating the blood vessels, slowing digestion, and moving blood flow to the heart, muscles, and brain.The autonomic nervous system controls the workings of internal organs such as the heart, lungs, digestive system, and endocrine systems it does so without conscious effort.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
